DNS zone file
dns zone file
Below is a table explaining the main elements of a DNS zone file in a simplified manner, using the ‘ddns365.com’ domain as an example.
| Element | Explanation |
|---|---|
| SOA(Start Of Authority) | The SOA record signifies the start of a DNS zone, containing the domain name and the email address of the administrator. For ‘ddns365.com’, ‘@’ represents ‘ddns365.com’ and the admin’s email uses ‘.’ instead of ‘@’. |
| Refresh, Retry, Expire, Minimum | These represent the period to check zone updates, the period to retry update checks, the time when zone data expires, and the TTL for negative caching, respectively. These are necessary for managing synchronization between name servers. |
| A(Address) | An A record is used to assign an IP address to a host. It defines which IP address the ‘ddns365.com’ domain or its subdomains actually point to. |
| TTL(Time to Live) | TTL in the Domain Name System (DNS) signifies how long an external name server stores the IP address of a certain domain in its cache. This allows for faster processing of requests for the same domain. |
| NS(Name Server) | An NS record indicates the name server of a certain domain. For instance, the name server for ‘ddns365.com’ could be ‘ns1.ddns365.com’. |
| MX(Mail Exchange) | An MX record is used to designate a mail server. It defines how mail is routed to a specific server. For ‘ddns365.com’, ‘mail.ddns365.com’ could be the mail server. |
| CNAME(Canonical Name) | A CNAME record is used to assign an alias to a host name. This allows multiple host names to be connected to one IP address. For example, ‘www.ddns365.com‘ could point to ‘ddns365.com’. |
| PTR(Pointer) | A PTR record is used to map an IP address to a domain name. This is primarily used for reverse DNS lookups. |
| SRV(Service) | An SRV record is used to specify where a certain service is available, including the domain, port, and protocol. This makes service discovery easier. |
| TXT(Text) | A TXT record is used to store arbitrary text. It’s commonly used in mail authentication mechanisms such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance). |
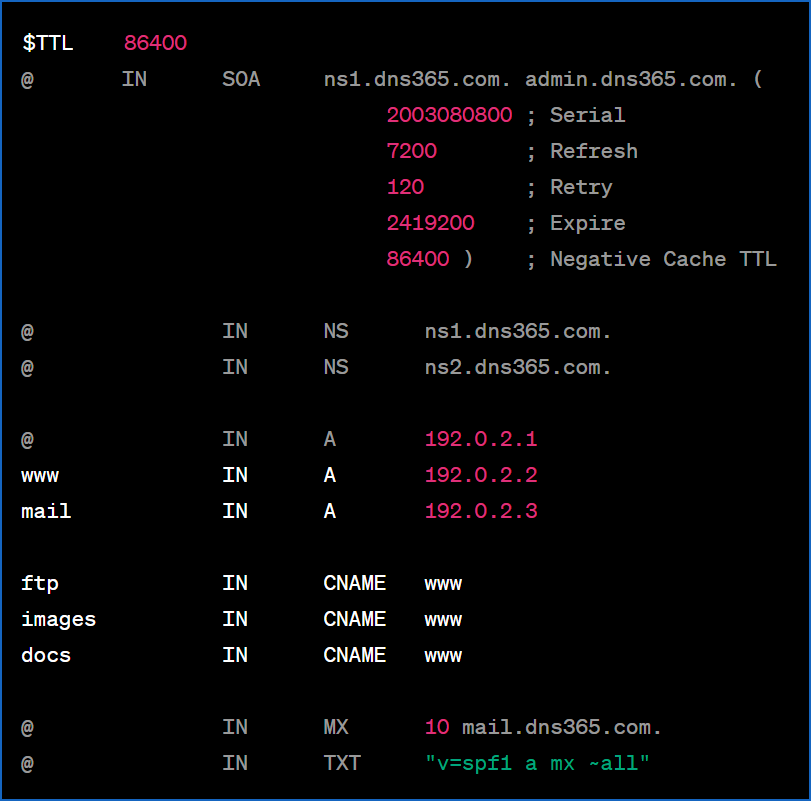
dns zone file includes the following records
- SOA record: Indicates the start of the zone. In this case, ns1.dns365.com is the Primary NS and admin.dns365.com is the zone administrator.
- NS records: Indicate that ns1.dns365.com and ns2.dns365.com are the name servers for this domain.
- A records: Indicate that dns365.com, www.dns365.com, and mail.dns365.com point to the IP addresses 192.0.2.1, 192.0.2.2, and 192.0.2.3 respectively.
- CNAME records: Indicate that ftp.dns365.com, images.dns365.com, and docs.dns365.com all point to www.dns365.com.
- MX record: Specifies that mail.dns365.com is used as the mail exchange server.
- TXT record: Contains the SPF record “v=spf1 a mx ~all”, indicating the policy for sending mail.
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA ns1.dns365.com. admin.dns365.com. (
2003080800 ; Serial
7200 ; Refresh
120 ; Retry
2419200 ; Expire
86400 ) ; Negative Cache TTL
@ IN NS ns1.dns365.com.
@ IN NS ns2.dns365.com.
@ IN A 192.0.2.1
www IN A 192.0.2.2
mail IN A 192.0.2.3
ftp IN CNAME www
images IN CNAME www
docs IN CNAME www
@ IN MX 10 mail.dns365.com.
@ IN TXT “v=spf1 a mx ~all”
dns zone file 존파일 한글 설명 및 예제
아래 표는 DNS 존파일의 주요 구성 요소에 대해 상세하게 설명한 것입니다. 그 중 ‘ddns365.com’ 도메인이 사용되었습니다.
| 요소 | 상세설명 |
|---|---|
| SOA(Start Of Authority) | SOA 레코드는 DNS 존의 시작을 표시하고, 도메인 이름과 관리자 이메일 주소를 포함합니다. ‘ddns365.com’의 경우 ‘@’는 ‘ddns365.com’를 가리키며, 관리자 이메일은 ‘@’ 대신 ‘.’을 사용하여 표시됩니다. |
| Refresh, Retry, Expire, Minimum | 이들은 각각 존의 업데이트 확인 주기, 업데이트 확인 재시도 주기, 존 정보가 만료되는 시간, 네거티브 캐싱 TTL을 나타냅니다. 이들은 네임서버 간의 동기화를 관리하는데 필요합니다. |
| A(Address) | A 레코드는 호스트에 IP 주소를 지정하는데 사용됩니다. ‘ddns365.com’ 도메인 또는 하위 도메인이 실제로 어떤 IP 주소를 가리키는지를 정의합니다. |
| TTL(Time to Live) | TTL은 도메인 이름 시스템(DNS)에서 외부 네임서버가 특정 도메인의 IP 주소를 캐시에 저장하는 시간을 나타냅니다. 이를 통해 동일한 도메인에 대한 요청을 더 빠르게 처리할 수 있습니다. |
| NS(Name Server) | NS 레코드는 해당 도메인의 네임서버를 나타냅니다. 예를 들어, ‘ddns365.com’의 네임서버는 ‘ns1.ddns365.com’일 수 있습니다. |
| MX(Mail Exchange) | MX 레코드는 메일서버를 지정하는데 사용됩니다. 이는 메일이 특정 서버로 라우팅되는 방식을 정의합니다. ‘ddns365.com’의 경우, ‘mail.ddns365.com’이 메일 서버일 수 있습니다. |
| CNAME(Canonical Name) | CNAME 레코드는 호스트 이름에 별칭을 부여하는데 사용됩니다. 이를 통해 하나의 IP 주소에 여러 호스트 이름을 연결할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, ‘www.ddns365.com’이 ‘ddns365.com’을 가리킬 수 있습니다. |
| PTR(Pointer) | PTR 레코드는 IP 주소에서 도메인 이름으로의 매핑을 수행하는 데 사용됩니다. 이는 주로 역 DNS 조회에 사용됩니다. |
| SRV(Service) | SRV 레코드는 특정 서비스가 어떤 도메인, 포트, 그리고 프로토콜에서 사용 가능한지를 지정하는데 사용됩니다. 이를 통해 서비스 발견이 용이해집니다. |
| TXT(Text) | TXT 레코드는 임의의 텍스트를 저장하는 데 사용됩니다. 이는 주로 SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)과 같은 메일 인증 메커니즘에 사용됩니다. |

이 파일에는 다음과 같은 레코드가 포함되어 있습니다:
- SOA 레코드: 존의 시작을 나타내며, ns1.dns365.com이 Primary NS이고 admin.dns365.com이 존의 관리자입니다.
- NS 레코드: ns1.dns365.com과 ns2.dns365.com이 해당 도메인의 네임서버임을 나타냅니다.
- A 레코드: dns365.com, www.dns365.com, mail.dns365.com 각각이 192.0.2.1, 192.0.2.2, 192.0.2.3 IP 주소를 가리킵니다.
- CNAME 레코드: ftp.dns365.com, images.dns365.com, docs.dns365.com 각각이 www.dns365.com을 가리킵니다.
- MX 레코드: 메일 교환 서버로 mail.dns365.com을 사용합니다.
- TXT 레코드: SPF 레코드로 “v=spf1 a mx ~all”를 포함하고 있어 메일 발신에 관한 정책을 나타냅니다.
궁금한 사항이 있으면 리눅스맨에게 톡톡 보내주세요
.
목차
